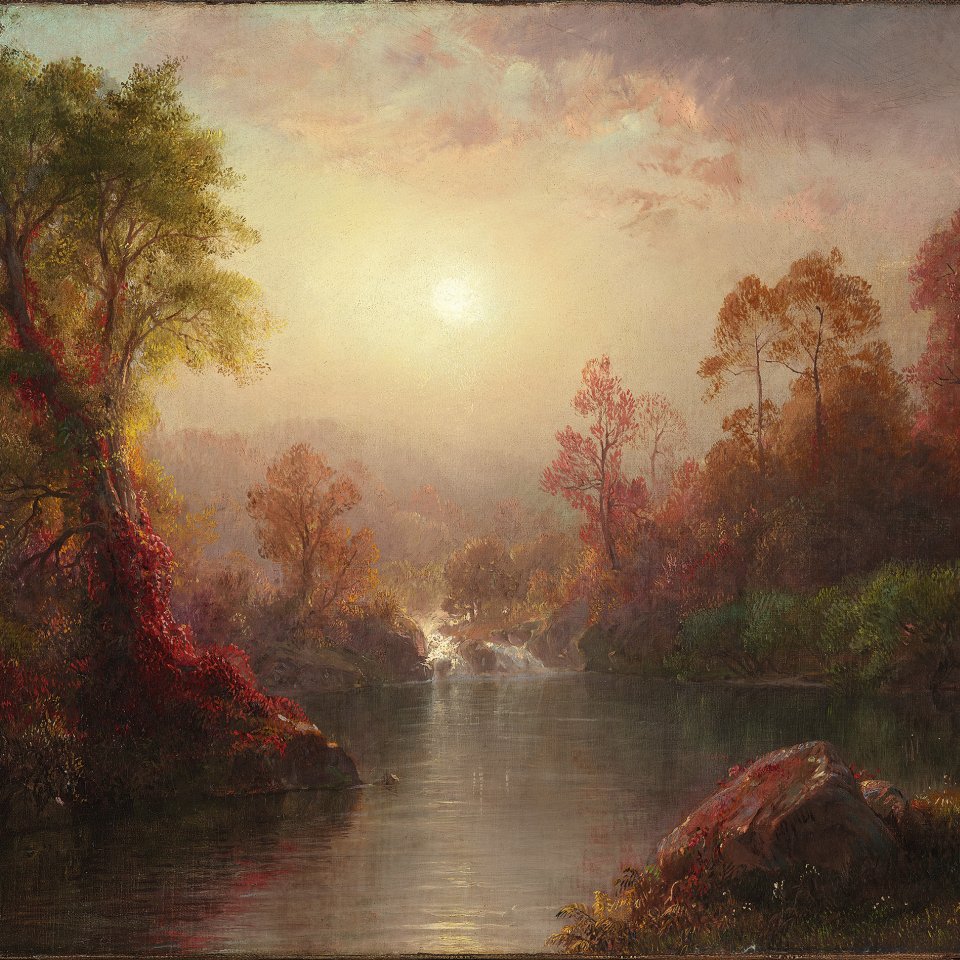
Portrait of Millicent, Duchess of Sutherland
John Singer Sargent lived in Paris until 1886. He studied with the painter Carolus Duran and made friends with a number of the Impressionists. His career took a radical turn following the scandal arising from the display at the 1884 Salon of his portrait of Madame Gautrier, a work known as Madame X. Sargent’s trips to the United States (1887-1888 and 1890) and to London (1893) brought him greater fame and new clients, and he was highly regarded on both sides of the Atlantic.
The present sitter, the Duchess of Sutherland, was one of the most celebrated and progressive members of London society. Sargent depicts her impressive form in a shady garden. With one hand resting on a fountain, she wears a green, floral pattern dress with a low-cut neckline. The Duchess seems to emerge from the natural world itself, which inspires the laurel leaf tiara on her red hair. The sources for this monumental composition extend from the great masters of the past that Sargent studied, including Velázquez and Van Dyck, to the 18th-century English portraitists.
CM
Millicent Saint Clair Erskine (1867‒1955) was the eldest daughter of the fourth Earl of Rosslin and Blanche Fitzroy. At the age of seventeen she had married Cromartie Sutherland Leveson-Gower, who inherited the title of Duke of Sutherland in 1892. As the lady of Stafford House in London, located opposite Buckingham Palace, and of Dunrobin Castle in Scotland, the duchess became one of the leading hostesses of the period and one of the most brilliant women in London society of the day. Known as a writer and an indefatigable charity worker devoted to the most underprivileged social classes, she was admired for her intelligence, beauty, elegance and moral stature. She was even awarded the French Croix de Guerre for her work as a nurse and generous contributions during the First World War. Sargent handles the character of Lady Millicent, then thirtyseven, with great sensitivity and delicacy. He portrays her full length, with the poise of an aristocrat, and skilfully captures her energetic personality and powerful gaze. In an outdoor setting the model, elegantly dressed, rests her right hand on a fountain and turns her erectly held body slightly towards the viewer, in a pose that recalls the English painter Sir Joshua Reynolds’s portraits of English duchesses in the guise of classical goddesses.
When it was shown at the annual exhibition of the Royal Academy of London in 1904, Roger Fry, who would soon become an advocate of Post-Impressionism, made an unfavourable comment about the portrait in an unsigned article published in the magazine Athenaeum. In contrast, other critics responded very positively to his eighteenth-century style: “The pleasure produced by the first sight of a masterpiece by Gainsborough or Reynolds or Romney, fresh from the easel, must have been somewhat akin to the glow of the eye’s delight at the splendour of John Sargent’s ‘The Duchess of Sutherland, ’” wrote an anonymous author in Academy. The historian and writer Henry Adams, who viewed the portrait in Paris in 1905, wrote to his beloved Elizabeth Cameron, “We sat half an hour before it; as usual, my eyes quite fascinated by it. Never did any artist paint such psychology as Sargent.”
Paloma Alarcó
Emotions through art
This artwork is part of a study we conducted to analyze people's emotional responses when observing 125 pieces from the museum.